Configure Health Alerts
Quick Start Guide
What You'll Learn
In 5 minutes, you'll know how to edit existing alerts, create new ones, and reload your configuration without downtime.
Get Started in 3 Steps
Step 1: Find Your Config Directory
Navigate to your Netdata config directory
Step 2: Edit an Alert
sudo ./edit-config health.d/cpu.conf
Step 3: Apply Changes
sudo netdatacli reload-health
Key Concept
You can highly configure Netdata's health watchdog with support for dynamic thresholds, hysteresis, alert templates, and more. You can customize any existing alerts based on your infrastructure's topology or specific monitoring needs or create entirely new entities.
You can use health alerts with any of Netdata's collectors (see the supported collector list) to monitor your systems, containers, and applications in real time.
While you can view active alerts on both the local dashboard and Netdata Cloud, you configure all health alerts per node via individual Netdata Agents. If you want to deploy a new alert across your infrastructure, you must configure each node with the same health configuration files.
Next Steps: Jump to Common Tasks for specific workflows or continue reading for comprehensive guidance.
Common Tasks
What You'll Learn
Step-by-step workflows for the most frequent alert configuration tasks.
Task 1: Modify Alert Thresholds
Why This Matters: Default thresholds may not fit your specific environment or requirements.
Quick Example:
# Change CPU warning from 85% to 75%
warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (60) : (75))
crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (75) : (85))
Step-by-Step:
- Find the alert file:
sudo ./edit-config health.d/cpu.conf - Locate the alert (e.g.,
10min_cpu_usage) - Modify
warnandcritlines - Save and reload:
sudo netdatacli reload-health
Task 2: Disable Unwanted Alerts
| Method | Use Case | Configuration File | How To |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disable all alerts | Testing/maintenance | netdata.conf | Set enabled = no in [health] section |
| Disable specific alerts | Remove noisy alerts | netdata.conf | Set enabled alarms = !alert_name * |
| Silence notifications | Keep monitoring, stop notifications | Alert config file | Change to: silent |
Task 3: Create a Simple Alert
Real-World Example: Monitor RAM usage above 80%
alarm: ram_usage
on: system.ram
lookup: average -1m percentage of used
units: %
every: 1m
warn: $this > 80
crit: $this > 90
info: RAM usage monitoring
Next Steps: See How-To Guides for detailed explanations.
How-To Guides
What You'll Learn
Detailed instructions for configuring, managing, and troubleshooting health alerts.
How to Reload Health Configuration
Why This Matters: You don't need to restart your Netdata Agent when making changes, preventing gaps in monitoring.
You don't need to restart your Netdata Agent when making changes to health configuration files, such as specific health entities. Instead, you can use netdatacli with the reload-health option to prevent gaps in metrics collection.
sudo netdatacli reload-health
Alternative Method:
If netdatacli doesn't work on your system, you can send a SIGUSR2 signal to the daemon, which reloads health configuration without restarting the entire process.
sudo killall -USR2 netdata
How to Edit Health Configuration Files
Configuration Locations:
Configuration Locations:
| Location | Purpose | Common Tasks | How to Edit |
|---|---|---|---|
netdata.conf [health] section | Global health settings | • Disable all monitoring (enabled = no)• Disable specific alerts • Change check frequencies | Edit directly or use edit-config |
health.d/*.conf files | Individual alert definitions | • Modify thresholds • Change notification recipients • Silence alerts ( to: silent) | Use edit-config health.d/filename.conf |
Navigate to your Netdata config directory and use edit-config to make changes to any of these files.
Edit Individual Alerts:
For example, to edit the cpu.conf health configuration file, run:
sudo ./edit-config health.d/cpu.conf
Understanding Alert Structure:
Each health configuration file contains one or more health entities, which always begin with alarm: or template:. Here's the first health entity in health.d/cpu.conf:
template: 10min_cpu_usage
on: system.cpu
class: Utilization
type: System
component: CPU
lookup: average -10m unaligned of user,system,softirq,irq,guest
units: %
every: 1m
warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (75) : (85))
crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (85) : (95))
delay: down 15m multiplier 1.5 max 1h
summary: CPU utilization
info: Average cpu utilization for the last 10 minutes (excluding iowait, nice and steal)
to: sysadmin
To customize this alert to trigger warning and critical alerts at lower CPU utilization levels, you can change the warn and crit lines to values of your choosing. For example:
warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (60) : (75))
crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (75) : (85))
Save the file and reload Netdata's health configuration to apply your changes.
How to Disable or Silence Alerts
Why This Matters: Different situations require different approaches to managing alerts - permanent removal, temporary silencing, or selective filtering.
You can disable alerts and notifications permanently via configuration changes, or temporarily via the health management API.
Disable All Alerts
Use Case: System maintenance or testing
In the netdata.conf [health] section, set enabled to no, and restart your Agent.
Disable Specific Alerts
Use Case: Remove known noisy or irrelevant alerts
In the netdata.conf [health] section, use pattern exclusion with enabled alarms = !oom_kill * to load all alerts except oom_kill.
You can also edit the file where the alert is defined, comment out its definition, and reload Netdata's health configuration.
Silence Individual Alert Notifications
Use Case: Keep monitoring active but stop notifications
You can stop receiving notifications for an individual alert by changing the to: line to silent in the alert's configuration file.
to: silent
This action requires that you reload Netdata's health configuration.
Temporary Runtime Control
Use Case: Scheduled maintenance or dynamic control
| Scenario | Solution | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Disable alerts during backups | Use health management API | API calls without config changes |
| Suppress notifications temporarily | Keep checks running, silence notifications | API control of notification system |
You can use the health management API to temporarily control alert behavior without changing configuration or restarting your Agent. The API allows you to:
- Disable all or some alerts from triggering during certain times (for instance, when running backups)
- Suppress notifications temporarily while keeping health checks running and alerts triggering
How to Write a New Health Entity
Why This Matters: While tuning existing alerts may work in some cases, you may need to write entirely new health entities based on how your systems, containers, and applications work.
Prerequisites: Read the Alert Configuration Reference for a complete listing of the format, syntax, and functionality of health entities.
Step-by-Step Process:
Step 1: Create the Configuration File
Navigate to your Netdata config directory, then use touch to create a new file in the health.d/ directory. Use edit-config to start editing the file.
As an example, let's create a ram-usage.conf file:
sudo touch health.d/ram-usage.conf
sudo ./edit-config health.d/ram-usage.conf
Step 2: Write Your Alert
Here's a health entity that triggers a warning alert when your node's RAM usage rises above 80%, and a critical alert above 90%:
alarm: ram_usage
on: system.ram
lookup: average -1m percentage of used
units: %
every: 1m
warn: $this > 80
crit: $this > 90
info: The percentage of RAM being used by the system.
Step 3: Understand Each Component
| Line | Purpose | This Example |
|---|---|---|
alarm | Entity name (alphanumeric, ., _ only) | ram_usage |
on | Chart to monitor | system.ram |
lookup | How to process metrics | Average last 1 minute, percentage of used dimension |
units | Display units | Percentages (%) |
every | Check frequency | Every 1 minute |
warn/crit | Trigger conditions | Warning > 80%, Critical > 90% |
info | Alert description | Appears in dashboard and notifications |
Understanding This Example
This health entity, named ram_usage, watches the system.ram chart. It looks up the last 1 minute of metrics from the used dimension and calculates the average of all those metrics in a percentage format, using % units. The entity performs this lookup every minute.
If the average RAM usage percentage over the last 1 minute is more than 80%, the entity triggers a warning alert. If the usage is more than 90%, the entity triggers a critical alert.
Step 4: Activate Your Alert
When you finish writing this new health entity, reload Netdata's health configuration to see it live on your local dashboard or Netdata Cloud.
Next Steps: Explore Alert Examples for more complex scenarios, or dive into the Alert Configuration Reference for complete syntax details.
Alert Configuration Reference
What You'll Learn
Complete syntax reference for all alert configuration options. Use this section when you need specific technical details.
Entity Types Overview
| Type | Label | Purpose | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alerts | alarm: | Attached to specific charts | Monitor specific server's CPU |
| Templates | template: | Apply to all charts of a context | Monitor all network interfaces |
Alerts are attached to specific charts and use the alarm label.
Templates define rules that apply to all charts of a specific context, and use the template label. Templates help you apply one entity to all disks, all network interfaces, all MySQL databases, and so on.
Precedence
Alarms are processed before templates. If you have alarm and template entities with the same name that both match the same chart, only the alarm will create an active alert for that chart.
For complete details on configuration loading order and precedence rules, see Alert Configuration Ordering.
Required vs Optional Configuration
Configuration Requirements
- The
alarmortemplateline must be the first line of any entity - The
online is always required - The
everyline is required if not usinglookup - Each entity must have at least one of the following lines:
lookup,calc,warn, orcrit
Special Syntax Rules:
- A few lines use space-separated lists to define how the entity behaves. You can use
*as a wildcard or prefix with!for a negative match. Order is important! See our simple patterns docs for more examples - Lines terminated by a
\are spliced together with the next line. The backslash is removed, and the following line is joined with the current one. No space is inserted, so you can split a line anywhere, even in the middle of a word. This is handy if yourinfoline consists of several sentences
Complete Configuration Reference
| line | required | functionality |
|---|---|---|
alarm/template | yes | Name of the alert/template |
on | yes | The chart this alert should attach to |
class | no | The general alert classification |
type | no | What area of the system the alert monitors |
component | no | Specific component of the type of the alert |
lookup | yes | The database lookup to find and process metrics for the chart specified through on |
calc | yes (see above) | A calculation to apply to the value found via lookup or another variable |
every | no | The frequency of the alert |
green/red | no | Set the green and red thresholds of a chart |
warn/crit | yes (see above) | Expressions evaluating to true or false, and when true, will trigger the alert |
to | no | A list of roles to send notifications to |
exec | no | The script to execute when the alert changes status |
delay | no | Optional hysteresis settings to prevent floods of notifications |
repeat | no | The interval for sending notifications when an alert is in WARNING or CRITICAL mode |
options | no | Add an option to not clear alerts |
host labels | no | Restrict an alert or template to a list of matching labels present on a host |
chart labels | no | Restrict an alert or template to a list of matching labels present on a chart |
summary | no | A brief description of the alert |
info | no | A longer text field that provides more information about this alert |
Configuration Line Details
Alert Line alarm or template
Purpose: This line starts an alert or template based on the entity type you want to create.
Alert Syntax:
alarm: NAME
Template Syntax:
template: NAME
Naming Rules:
NAMEcan be any alphanumeric character- Only
.(period) and_(underscore) symbols allowed - Can’t be
chart name,dimension name,family name, orchart variable names
Alert Line on
Purpose: This line defines the chart this alert should attach to.
For Alerts:
on: CHART
The value CHART should be the unique ID or name of the chart you're interested in, as shown on the dashboard. In the image below, the unique ID is system.cpu.
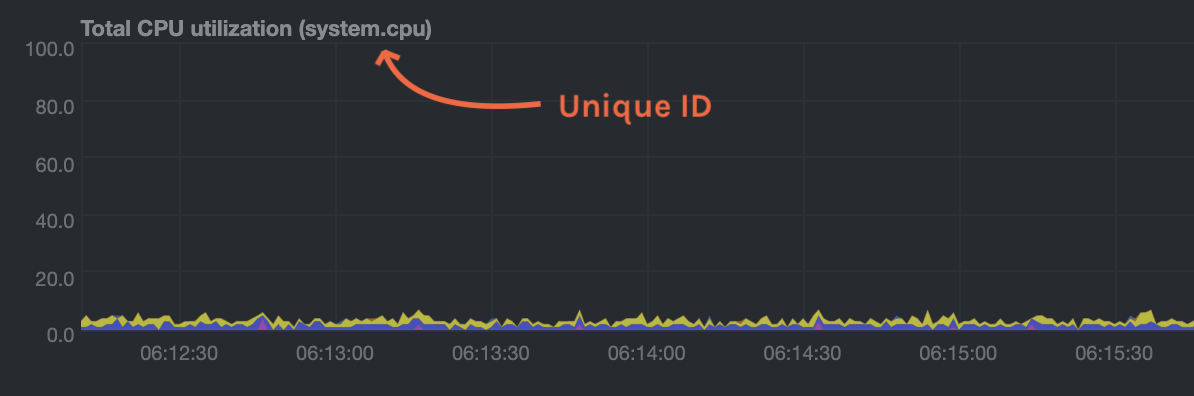
For Templates:
on: CONTEXT
The value CONTEXT should be the context you want this template to attach to.
Finding the Context
Need to find the context? Hover over the date on any given chart and look at the tooltip. In the image below, which shows a disk I/O chart, the tooltip reads: proc:/proc/diskstats, disk.io.
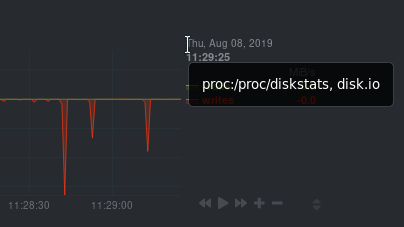
You're interested in what comes after the comma: disk.io. That's the name of the chart's context.
If you create a template using the disk.io context, it will apply an alert to every disk available on your system.
Alert Line class
Purpose: This indicates the type of error (or general problem area) that the alert or template applies to.
Example Use: Latency can be used for alerts that trigger on latency issues on network interfaces, web servers, or database systems.
class: Latency
Available Classes:
| Class | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Errors | Error rate monitoring |
| Latency | Response time issues |
| Utilization | Resource usage monitoring |
| Workload | Load and throughput monitoring |
class will default to Unknown if the line is missing from the alert configuration.
Alert Line type
Purpose: You can use type to indicate the broader area of the system that the alert applies to.
Example: Under the general Database type, you can group together alerts that operate on various database systems, like MySQL, CockroachDB, CouchDB, etc.
type: Database
Available Types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Ad Filtering | Services related to Ad Filtering (like pi-hole) |
| Certificates | Certificate monitoring related |
| Cgroups | Alerts for CPU and memory usage of control groups |
| Computing | Alerts for shared computing applications (e.g. boinc) |
| Containers | Container related alerts (e.g. docker instances) |
| Database | Database systems (e.g. MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc) |
| Data Sharing | Used to group together alerts for data sharing applications |
| DHCP | Alerts for DHCP related services |
| DNS | Alerts for DNS related services |
| Kubernetes | Alerts for kubernetes nodes monitoring |
| KV Storage | Key-Value pairs services alerts (e.g. memcached) |
| Linux | Services specific to Linux (e.g. systemd) |
| Messaging | Alerts for message passing services (e.g. vernemq) |
| Netdata | Internal Netdata components monitoring |
| Other | When an alert doesn't fit in other types |
| Power Supply | Alerts from power supply related services (e.g. apcupsd) |
| Search engine | Alerts for search services (e.g. elasticsearch) |
| Storage | Class for alerts dealing with storage services (storage devices typically live under System) |
| System | General system alerts (e.g. CPU, network, etc.) |
| Virtual Machine | Virtual Machine software |
| Web Proxy | Web proxy software (e.g. squid) |
| Web Server | Web server software (e.g. Apache, nginx, etc.) |
| Windows | Alerts for monitoring Windows services |
If an alert configuration is missing the type line, its value will default to Unknown.
Alert Line component
Purpose: You can use component to narrow down what the previous type value specifies for each alert or template.
Example: Continuing from the previous example, component might include MySQL, CockroachDB, MongoDB, all under the same Database type.
component: MySQL
As with the class and type lines, if component is missing from the configuration, its value will default to Unknown.
Alert Line lookup
Purpose: This line makes a database lookup to find a value. The result of this lookup is available as $this.
Full Syntax:
lookup: METHOD(GROUPING OPTIONS) AFTER [at BEFORE] [every DURATION] [OPTIONS] [of DIMENSIONS]
Required Parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
METHOD | Grouping method | average, min, max |
AFTER | How far back to look (negative number) | -1m, -1h, -1d |
Optional Parameters:
| Parameter | Purpose | Details |
|---|---|---|
GROUPING OPTIONS | Conditional processing | CONDITION VALUE where condition is !=, =, ==, \<=, <, >, >= |
at BEFORE | End of lookup timeframe | Default is 0 (now) |
every DURATION | Update frequency | Supports s, m, h, d units |
OPTIONS | Processing modifiers | See options table below |
of DIMENSIONS | Which dimensions to include | Space-separated list, supports patterns |
Processing Options:
| Option | Effect |
|---|---|
percentage | Calculate percentage of selected dimensions over total |
absolute | Turn all sample values positive |
min | Return minimum of all dimensions after time-aggregation |
max | Return maximum of all dimensions after time-aggregation |
average | Return average of all dimensions after time-aggregation |
sum | Return sum of all dimensions (default) |
min2max | Return delta between min and max of dimensions |
unaligned | Prevent shifting query window to multiples of duration |
match-ids | Match dimensions by IDs (default) |
match-names | Match dimensions by names |
Example:
lookup: average -10m unaligned of user,system,softirq,irq,guest
This looks back 10 minutes, calculates the average of the specified CPU dimensions, without aligning to time boundaries.
The result of the lookup will be available as $this and $NAME in expressions. The timestamps of the timeframe evaluated by the database lookup are available as variables $after and $before (both are unix timestamps).
Alert Line calc
Purpose: You can design a calc to apply some calculation to the values or variables available to the entity.
Key Points:
- The result becomes available as
$thisvariable - Overwrites the value from your
lookup - Can be used without
lookupif using other available variables - Uses expressions for syntax
calc: EXPRESSION
When to Use:
- With
lookup: Perform calculation after database retrieval - Without
lookup: When using other available variables - For complex logic: Mathematical operations, conditions, transformations
Alert Line every
Purpose: Sets the update frequency of this alert.
every: DURATION
Supported Units:
sfor secondsmfor minuteshfor hoursdfor days
Example: every: 30s checks the alert every 30 seconds.
Alert Lines green and red
Purpose: Set the green and red thresholds of a chart for visualization.
green: NUMBER
red: NUMBER
Important Notes:
- Both values are available as
$greenand$redin expressions - If multiple alerts define different thresholds, the first alert's values are used
- For multiple threshold sets, use absolute numbers instead of variables
Alert Lines warn and crit
Purpose: Define the expressions that trigger warning or critical alerts.
warn: EXPRESSION
crit: EXPRESSION
Key Points:
- Optional (but you need at least one)
- Should evaluate to true/false (or zero/non-zero)
- Uses Netdata's expression syntax
- Can reference variables like
$this,$green,$red
Examples:
warn: $this > 80
crit: $this > 95
Alert Line to
Purpose: Specifies who receives notifications when the alert changes status.
to: ROLE1 ROLE2 ROLE3 ...
How It Works:
- First parameter passed to the
execscript - Default script (
alarm-notify.sh) treats this as a space-separated list of roles - Roles are consulted to find exact recipients per notification method
Alert Line exec
Purpose: Script to execute when the alert status changes.
exec: SCRIPT
Default Behavior:
- Default script is Netdata's
alarm-notify.sh - Supports all notification methods Netdata supports
- Includes custom hooks
Alert Line delay
Purpose: Provide optional hysteresis settings to prevent notification floods.
These settings don't affect the actual alert - only when the exec script is executed.
Full Syntax:
delay: [[[up U] [down D] multiplier M] max X]
Parameters:
| Parameter | Purpose | Default |
|---|---|---|
up U | Delay for status increases (CLEAR→WARNING, WARNING→CRITICAL) | 0 |
down D | Delay for status decreases (CRITICAL→WARNING, WARNING→CLEAR) | 0 |
multiplier M | Multiplies U and D when alert changes state during delay | 1.0 |
max X | Maximum absolute notification delay | max(U×M, D×M) |
Example with Timeline:
delay: up 10s down 15m multiplier 2 max 1h
Starting at 00:00:00 with CLEAR status:
| Time | New Status | Delay Applied | Notification At | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00:00:01 | WARNING | up 10s | 00:00:11 | First state switch |
| 00:00:05 | CLEAR | down 15m x2 | 00:30:05 | Alert changed during delay, so multiplied |
| 00:00:06 | WARNING | up 10s x2 x2 | 00:00:26 | Multiplied twice |
Alert Line repeat
Purpose: Defines the interval between repeating notifications for alerts in CRITICAL or WARNING mode.
repeat: [off] [warning DURATION] [critical DURATION]
Options:
| Option | Effect |
|---|---|
off | Turns off repeating for this alert |
warning DURATION | Repeat interval for WARNING state (use 0s to disable) |
critical DURATION | Repeat interval for CRITICAL state (use 0s to disable) |
Why Use This: Overrides default repeat settings from netdata.conf health configuration.
Alert Line options
Purpose: Special alert behavior options.
options: no-clear-notification
Available Options:
no-clear-notification- Prevents clearing the alert notification
When to Use no-clear-notification:
- Alerts comparing two time frames (e.g., last 3 minutes vs last hour)
- When newer data might "pollute" the baseline comparison
- When clearing conditions are unreliable due to data characteristics
Example Use Case: HTTP response time alert comparing recent average to historical average - as time passes, the recent slow responses become part of the historical data, making the alert appear "cleared" even though the underlying issue wasn't resolved.
Alert Line host labels
Purpose: Restricts alerts to hosts with matching labels.
Prerequisites: See our host labels guide for setup instructions.
Example Configuration:
[host labels]
installed = 20191211
room = server
Usage in Alerts:
host labels: room = server
Pattern Support:
host labels: installed = 201* # Matches all hosts installed in 2010s
How It Works:
- Space-separated list
- Accepts simple patterns
- Alert only loads on matching hosts
Alert Line chart labels
Purpose: Filters alerts based on chart labels.
How to Find Chart Labels: Check http://localhost:19999/api/v1/charts?all
Example Use Case:
Each disk_space chart has a mount_point label. To exclude external disk alerts:
chart labels: mount_point=!/mnt/disk1 *
Multiple Label Logic:
chart labels: mount_point=/mnt/disk1 device=sda
This requires BOTH conditions to be true (AND logic).
Important Notes:
- Space-separated list with simple patterns support
- If a specified label doesn't exist on the chart, the chart won't match
- Multiple labels use AND logic
Alert Line summary
Purpose: Brief title of the alert used in notifications and dashboard.
summary: Available Ram
Variable Support:
| Variable | Replaced With |
|---|---|
${family} | Family instance (e.g., eth0) |
${label:LABEL_NAME} | Chart label value |
Example with Variables:
summary: 1 minute received traffic overflow for ${label:device}
Renders as: 1 minute received traffic overflow for eth0
Variable names are case-sensitive.
Alert Line info
Purpose: Detailed description of the alert for notifications and UI elements.
info: Percentage of estimated amount of RAM available for userspace processes, without causing swapping
Variable Support:
| Variable | Replaced With |
|---|---|
${family} | Family instance (e.g., eth0) |
${label:LABEL_NAME} | Chart label value |
Examples with Variables:
Family Variable:
info: average inbound utilization for the network interface ${family} over the last minute
Renders as: average inbound utilization for the network interface eth0 over the last minute
Label Variable:
info: average ratio of HTTP responses with unexpected status over the last 5 minutes for the site ${label:target}
Renders as: average ratio of HTTP responses with unexpected status over the last 5 minutes for the site https://netdata.cloud/
Next Steps: Continue to Expressions and Variables to understand the calculation syntax, or jump to Alert Examples for practical implementations.
Expressions and Variables
What You'll Learn
How to write calculations and use variables in your alert definitions. Essential for creating custom logic and accessing chart data.
Expressions Overview
Why This Matters: Netdata has an internal infix expression parser that allows you to create complex alert logic using mathematical operations, comparisons, and conditional statements.
Supported Operators:
| Type | Operators | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Arithmetic | +, -, *, / | Numeric values |
| Comparison | <, ==, \<=, <>, !=, >, >= | 1 (true) or 0 (false) |
| Logical | &&, ` |
Special Functions:
abs()- Absolute value(condition) ? (true_expr) : (false_expr)- Conditional operator
Special Values:
| Value | Purpose | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
nan | Not a number (database lookup failed) | $this != nan |
inf | Infinite (division by zero) | $this != inf |
Conditional Operator for Hysteresis
Why This Matters: The conditional operator (? :) can create "sticky" alert thresholds that prevent alert spam when values fluctuate around a threshold. This is called hysteresis.
Basic Pattern:
warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (lower_threshold) : (higher_threshold))
Real Example - CPU Usage Alert:
warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (75) : (85))
crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (85) : (95))
How This Works:
| Alert State | Triggers At | Clears At | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warning | 85% CPU | 75% CPU | Creates 10% buffer - CPU must drop below 75% to clear warning |
| Critical | 95% CPU | 85% CPU | Creates 10% buffer - CPU must drop below 85% to return to warning |
Benefits:
- Quick alerting when issues arise
- Protection against spam when values hover near thresholds
- Single initial notification instead of constant alerts during fluctuation
Example Scenario: If CPU usage fluctuates between 80–90%, you'll receive just one initial warning, rather than constant notifications.
Variables Reference
How to Find Available Variables:
You can find all variables for a given chart using: http://NODE:19999/api/v1/alarm_variables?chart=CHART_NAME
Example: Variables for the system.cpu chart
Chart vs Template Variables
Although the alarm_variables link shows variables for a particular chart, the same variables can also be used in templates for charts belonging to a given context. All charts of a given context are essentially identical, with the only difference being the family that identifies a particular hardware or software instance.
Variable Categories
Chart Local Variables
What's Available:
- All chart dimensions as variables (e.g.,
$user,$systemfor CPU chart) - Values from other configured alerts on the same chart
- Special chart variables (see table below)
Special Chart Variables:
| Variable | Contains |
|---|---|
$last_collected_t | Unix timestamp of last data collection |
$collected_total_raw | Sum of all dimensions (last collected values) |
$update_every | Update frequency of the chart |
$green, $red | Thresholds defined in alerts |
Dimension Value Types:
- Default: Last calculated (interpolated) value as shown on charts
- Raw suffix:
$dimension_raw- Last collected value - Timestamp suffix:
$dimension_last_collected_t- Unix timestamp when dimension was last collected
Host Variables
What's Available: All dimensions of all charts, including all alerts, in fullname format.
Format: CHART.VARIABLE
CHARTcan be either chart ID or chart name- Both formats are supported
Examples:
$system.cpu.user- User CPU from system.cpu chart$disk.sda.reads- Read operations from sda disk chart
Special Variables
| Variable | Contains | Usage |
|---|---|---|
$this | Current alert value | Result of calc line or current alert |
$status | Current alert status | Compare with status constants |
$now | Current unix timestamp | Time-based calculations |
Alert Status Constants:
| Constant | Numeric Value | Usage |
|---|---|---|
$REMOVED | -2 | Alert deleted (SIGUSR2 reload) |
$UNINITIALIZED | -1 | Alert not initialized |
$UNDEFINED | 0 | Calculation failed |
$CLEAR | 1 | Alert OK/not triggered |
$WARNING | 2 | Warning condition met |
$CRITICAL | 3 | Critical condition met |
Status Comparison Examples:
# Check if alert is in warning or higher
warn: $status >= $WARNING
# Check if alert is specifically critical
crit: $status == $CRITICAL
Status values increase with severity, so $status > $CLEAR will match both WARNING and CRITICAL states.
Alert Status Lifecycle
Status Flow: UNINITIALIZED → UNDEFINED/CLEAR → WARNING → CRITICAL
When Status Changes:
REMOVED- Alert deleted during configuration reloadUNINITIALIZED- Alert created but not yet calculatedUNDEFINED- Database lookup failed, division by zero, etc.CLEAR- Alert conditions aren’t met (normal state)WARNING- Warning expression returned true/non-zeroCRITICAL- Critical expression returned true/non-zero
Script Execution: The external script (exec line) is called for ALL status changes.
Next Steps: Ready to see these concepts in action? Continue to Alert Examples for practical implementations.
Alert Examples
What You'll Learn
Real-world alert configurations that demonstrate different monitoring scenarios. Use these as templates for your own alerts.
Example 1: Server Alive Check
Scenario: Monitor if the Apache server is collecting data properly.
Why This Matters: Detect when data collection stops, indicating potential server or network issues.
template: apache_last_collected_secs
on: apache.requests
calc: $now - $last_collected_t
every: 10s
warn: $this > ( 5 * $update_every)
crit: $this > (10 * $update_every)
How It Works:
| Component | Purpose | This Example |
|---|---|---|
template | Applies to all Apache servers | apache_last_collected_secs |
on | Chart context to monitor | apache.requests |
calc | Time since last data collection | $now - $last_collected_t |
every | Check frequency | Every 10 seconds |
warn | Warning threshold | 5 missed collection cycles |
crit | Critical threshold | 10 missed collection cycles |
Variables Used:
$now- Current timestamp$last_collected_t- Last data collection timestamp$update_every- Chart update frequency$this- Result of calculation (seconds since last collection)
Example 2: Disk Space Monitoring
Scenario: Alert when any disk is running low on space.
Why This Matters: Prevent system failures due to full disks.
template: disk_full_percent
on: disk.space
calc: $used * 100 / ($avail + $used)
every: 1m
warn: $this > 80
crit: $this > 95
repeat: warning 120s critical 10s
How It Works:
| Component | Purpose | This Example |
|---|---|---|
template | Applies to all disks | disk_full_percent |
on | Chart context | disk.space |
calc | Calculate usage percentage | $used * 100 / ($avail + $used) |
warn/crit | Simple thresholds | 80% warning, 95% critical |
repeat | Notification frequency | Every 2min (warning), 10sec (critical) |
Variables Used:
$used- Used disk space dimension$avail- Available disk space dimension
Example 3: Predictive Disk Full Alert
Scenario: Predict when disks will run out of space based on the current fill rate.
Why This Matters: Get warning before disk space becomes critical.
Step 1: Calculate Disk Fill Rate
template: disk_fill_rate
on: disk.space
lookup: max -1s at -30m unaligned of avail
calc: ($this - $avail) / (30 * 60)
every: 15s
Step 2: Predict Hours Until Full
template: disk_full_after_hours
on: disk.space
calc: $avail / $disk_fill_rate / 3600
every: 10s
warn: $this > 0 and $this < 48
crit: $this > 0 and $this < 24
How It Works:
| Step | Purpose | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Calculate fill rate | (space_30min_ago - current_space) / 1800_seconds |
| 2 | Predict time to full | current_available / fill_rate / 3600 |
Logic:
- Only positive predictions matter (disk filling up)
- Warning: Less than 48 hours of space remaining
- Critical: Less than 24 hours of space remaining
Example 4: Network Packet Drops
Scenario: Alert on any network packet drops.
Why This Matters: Packet drops indicate network issues that could affect performance.
template: 30min_packet_drops
on: net.drops
lookup: sum -30m unaligned absolute
every: 10s
crit: $this > 0
How It Works:
| Component | Purpose | This Example |
|---|---|---|
template | Applies to all network interfaces | 30min_packet_drops |
lookup | Sum drops over 30 minutes | sum -30m unaligned absolute |
crit | Any drops trigger critical | $this > 0 |
Key Points:
- The drops chart only exists when packets are dropped
- The alert automatically attaches when the first drop is detected
- Zero tolerance for packet loss
Example 5: Z-Score Based Alert
Scenario: Detect CPU usage anomalies using statistical analysis.
Why This Matters: Identify unusual patterns that fixed thresholds might miss.
alarm: cpu_user_mean
on: system.cpu
lookup: mean -60s of user
every: 10s
alarm: cpu_user_stddev
on: system.cpu
lookup: stddev -60s of user
every: 10s
alarm: cpu_user_zscore
on: system.cpu
lookup: mean -10s of user
calc: ($this - $cpu_user_mean) / $cpu_user_stddev
every: 10s
warn: $this < -2 or $this > 2
crit: $this < -3 or $this > 3
How It Works:
| Alert | Purpose | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
cpu_user_mean | Calculate average CPU usage | Mean over 60 seconds |
cpu_user_stddev | Calculate variability | Standard deviation over 60 seconds |
cpu_user_zscore | Detect anomalies | (current - mean) / stddev |
Z-Score Interpretation:
- ±2: Moderately unusual (warning)
- ±3: Highly unusual (critical)
- Negative: Below normal
- Positive: Above normal
Example 6: Machine Learning Anomaly Detection
Scenario: Use Netdata's built-in ML for chart-level anomaly detection.
Why This Matters: Detect complex patterns across multiple metrics without manual threshold tuning.
template: ml_5min_cpu_chart
on: system.cpu
lookup: average -5m anomaly-bit of *
calc: $this
units: %
every: 30s
warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (5) : (20))
crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (20) : (100))
info: rolling 5min anomaly rate for system.cpu chart
How It Works:
| Component | Purpose | This Example |
|---|---|---|
lookup | Average anomaly rate across CPU dimensions | 5-minute rolling window |
| Hysteresis | Prevent alert flapping | Warning: 20%→5%, Critical: 100%→20% |
anomaly-bit | ML-generated anomaly indicators | 0 (normal) or 1 (anomalous) |
Example 7: Node-Level ML Monitoring
Scenario: Monitor overall system health using ML across all metrics.
Why This Matters: Get a holistic view of system anomalies beyond individual charts.
template: ml_5min_node
on: anomaly_detection.anomaly_rate
lookup: average -5m of anomaly_rate
calc: $this
units: %
every: 30s
warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (5) : (20))
crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (20) : (100))
info: rolling 5min anomaly rate for all ML enabled dims
Key Differences from Chart-Level:
- Uses
anomaly_detection.anomaly_ratechart - Monitors
anomaly_ratedimension - Covers all ML-enabled dimensions across the node
Next Steps: Having trouble with your alerts? Continue to Troubleshooting for debugging techniques.
Troubleshooting
What You'll Learn
How to debug alert issues, understand why alerts aren't working, and get detailed information about alert processing.
Find Chart and Context Information
Finding Chart Names: You can find chart information in two places:
| Method | URL | Contains |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration | http://NODE:19999/netdata.conf | All chart details |
| API | http://NODE:19999/api/v1/charts | JSON chart data |
Replace NODE with your server's IP address or hostname.
Analyze Alert Expressions
Why This Matters: Understand how Netdata interprets your expressions and what values are being calculated.
Check Alert Processing:
Visit http://NODE:19999/api/v1/alarms?all to see:
- Original expression as written in config
- Parsed expression with added parentheses showing evaluation flow
- Current alert status and values
- Available variables and their values
Expression Evaluation Flow: Netdata adds parentheses to show how it evaluates your expressions:
Your Expression:
warn: $this > 80 and $status >= $WARNING
Netdata's Interpretation:
warn: (($this > 80) and ($status >= $WARNING))
Troubleshooting Decision Trees
How to Use These Decision Trees
Follow the flowcharts below to systematically diagnose and resolve alert issues. Each path leads to specific solutions with step-by-step instructions.
Decision Tree: Alert Not Working
Decision Tree: Alert Always Triggering
Decision Tree: Alert Flapping
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: Alert Not Triggering
Possible Causes:
| Problem | Check This | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Wrong chart name | on: line matches actual chart | Use chart ID from dashboard |
| Incorrect dimensions | Dimension names in lookup | Check available dimensions |
| Missing data | Chart has recent data | Verify data collection |
| Expression errors | Variables resolve correctly | Use /api/v1/alarm_variables |
Issue: Alert Always Triggering
Possible Causes:
| Problem | Check This | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Wrong threshold direction | > vs < in expressions | Review logic |
| Units mismatch | Comparing percentages to absolute values | Check calculation units |
| Variable name errors | $this vs $chart.dimension | Verify variable names |
Issue: Alert Flapping
Possible Causes:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Values near threshold | Implement hysteresis |
| Noisy data | Increase lookup time window |
| Too frequent checks | Increase every: interval |
Hysteresis Example:
# Instead of simple threshold
warn: $this > 80
# Use hysteresis
warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (75) : (80))
Issue: Variables Not Found
Debug Steps:
-
Check Available Variables:
http://NODE:19999/api/v1/alarm_variables?chart=CHART_NAME -
Verify Chart Context:
- For
alarm:use chart name - For
template:use chart context
- For
-
Check Variable Syntax:
- Chart local:
$dimension_name - Host variables:
$chart_name.dimension_name - Special variables:
$this,$now,$status
- Chart local:
Testing Alert Changes
Safe Testing Process:
-
Create Test File:
sudo touch health.d/test-alert.conf
sudo ./edit-config health.d/test-alert.conf -
Write Simple Alert:
alarm: test_ram
on: system.ram
lookup: average -1m percentage of used
every: 10s
war: $this > 50 # Low threshold for testing
info: Test alert - safe to ignore -
Reload and Monitor:
sudo netdatacli reload-health
# Watch dashboard for test alert appearance -
Remove When Done:
sudo rm health.d/test-alert.conf
sudo netdatacli reload-health
Performance Considerations
Alert Impact on System:
| Factor | Impact | Optimization |
|---|---|---|
Check frequency (every:) | CPU usage | Use appropriate intervals |
| Lookup timeframe | Memory/CPU | Don't use excessively long periods |
| Number of alerts | Overall performance | Disable unused alerts |
| Complex expressions | CPU per check | Simplify where possible |
Recommended Frequencies:
| Alert Type | Suggested Frequency | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Critical system metrics | 10-30s | Quick response needed |
| Resource usage | 1-5m | Trends matter more than instant values |
| Predictive alerts | 15m-1h | Based on longer-term patterns |
Getting Help
Information to Provide:
When seeking help, include:
-
Alert Configuration:
# Your complete alert definition -
Chart Information:
http://your-server:19999/api/v1/alarm_variables?chart=chart_name -
Current Status:
http://your-server:19999/api/v1/alarms?all
Community Resources:
Next Steps: You now have comprehensive knowledge of Netdata health configuration. Start with the Quick Start Guide for immediate needs or dive into Common Tasks for specific workflows.
Do you have any feedback for this page? If so, you can open a new issue on our netdata/learn repository.